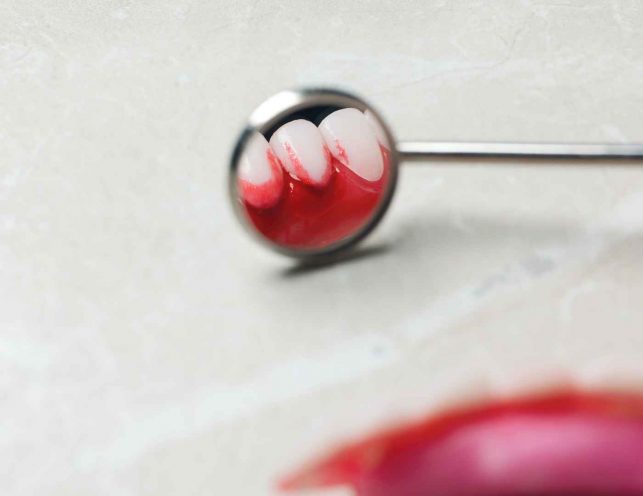
Understanding Bleeding Gums Causes
Bleeding gums can be a concerning symptom, often indicative of underlying oral health issues. However, it’s essential to recognize that bleeding gums can also be associated with broader health conditions. Here, we’ll explore the various potential causes of bleeding gums, including oral health-related factors and other systemic issues.
Common Causes of Bleeding Gums
Bleeding gums are frequently associated with oral health problems, such as:
- Gingivitis: Gingivitis is the initial stage of gum disease and is characterized by inflammation of the gums. Poor oral hygiene, including infrequent brushing and flossing, can lead to gingivitis.
- Periodontitis: When gingivitis is left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease. In periodontitis, the supporting bone and fibers that hold your teeth in place can be damaged.
- Smoking: Tobacco use, especially smoking, is a significant risk factor for gum disease. It can also reduce blood flow to the gums, impairing their ability to heal.
- Trench Mouth: Trench mouth, or necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis, is a severe form of gum disease characterized by painful, bleeding gums. It’s often associated with stress, poor nutrition, and compromised immune function.
Other potential causes of bleeding gums extend beyond oral health:
- Systemic Health Conditions: Certain medical conditions like diabetes, blood-clotting disorders, leukemia, and HIV/AIDS can lead to gum bleeding.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormone fluctuations during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause can make gums more susceptible to bleeding.
- Vitamin Deficiencies: Vitamin deficiencies, particularly vitamin C and vitamin K deficiencies, can affect gum health and lead to bleeding.
- Blood-Thinning Medications: Anticoagulant medications can increase the risk of bleeding gums.
Care and Treatment for Bleeding Gums
The treatment of bleeding gums depends on the underlying cause:
- For Gum Disease: If gum disease is the culprit, improved oral hygiene, antibiotics, tooth scaling and root planing, and sometimes surgical procedures may be recommended.
- For Other Health Conditions: If an underlying medical condition is responsible, your healthcare provider will address that condition with appropriate treatments.
Preventing Bleeding Gums
While you can’t always prevent bleeding gums related to systemic health conditions, there are steps you can take to reduce the risk of gum disease:
- Maintain excellent oral hygiene by brushing your teeth at least twice daily and flossing once a day.
- Use a soft-bristle toothbrush to avoid gum irritation.
- Rinse your mouth with warm saltwater or an antibacterial mouthwash.
- Avoid smoking, which is a significant risk factor for gum disease.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If your gums bleed consistently for more than two weeks, you should seek medical attention. Ignoring bleeding gums can lead to worsening oral health conditions or the progression of underlying medical issues. Don’t hesitate to consult your dentist or healthcare provider if you have concerns about bleeding gums or related symptoms like bad breath or swollen gums.
Bleeding gums can serve as an early warning sign of various health concerns. Timely evaluation and appropriate care can help you maintain good oral health and overall well-being.
learn more: